Difference between revisions of "ICTP cloud"
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
An example: | An example: | ||
ictptutor@smr3694test:~/YAMBO_TUTORIALS$ spack info yambo | |||
AutotoolsPackage: yambo | |||
Description: | |||
Description: | |||
YAMBO is an open-source code released within the GPL licence. YAMBO | YAMBO is an open-source code released within the GPL licence. YAMBO | ||
implements Many-Body Perturbation Theory (MBPT) methods (such as GW and | implements Many-Body Perturbation Theory (MBPT) methods (such as GW and | ||
| Line 64: | Line 62: | ||
Quantum ESPRESSO and Abinit. | Quantum ESPRESSO and Abinit. | ||
Homepage: http://www.yambo-code.org/index.php | Homepage: http://www.yambo-code.org/index.php | ||
Maintainers: @nicspalla | Maintainers: @nicspalla | ||
Externally Detectable: | Externally Detectable: | ||
False | False | ||
Tags: | Tags: | ||
None | None | ||
Preferred version: | Preferred version: | ||
5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master | 5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master | ||
Safe versions: | Safe versions: | ||
5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master | 5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master | ||
5.0.4 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.4.tar.gz | 5.0.4 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.4.tar.gz | ||
| Line 91: | Line 89: | ||
4.3.3 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.3.3.tar.gz | 4.3.3 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.3.3.tar.gz | ||
Deprecated versions: | Deprecated versions: | ||
None | None | ||
Variants: | Variants: | ||
Name [Default] When Allowed values Description | Name [Default] When Allowed values Description | ||
================= ============= ==================== | ================= ============= ==================== ========================================================================= | ||
cuda [off] -- on, off Build with CUDA | cuda [off] -- on, off Build with CUDA | ||
| Line 115: | Line 113: | ||
yambopy [off] -- on, off Install Yambopy package | yambopy [off] -- on, off Install Yambopy package | ||
Installation Phases: | Installation Phases: | ||
autoreconf configure build install | autoreconf configure build install | ||
Build Dependencies: | Build Dependencies: | ||
blas cuda fftw-api gnuconfig hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc | blas cuda fftw-api gnuconfig hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc | ||
Link Dependencies: | Link Dependencies: | ||
blas cuda fftw-api hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc | blas cuda fftw-api hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc | ||
Run Dependencies: | Run Dependencies: | ||
None | None | ||
Virtual Packages: | Virtual Packages: | ||
None | None | ||
Revision as of 15:45, 29 March 2022
A the participants of the computational school on "Ab-initio Many-body Methods and Simulations with the Yambo Code" will be sent a link and a password to connect via noVNC to a Virtual Machine running on the ICTP cloud server. This is the strongly suggested mode to work on the hand-on sessions. noVNC is a open source VNC (Virtual Network Computing, a graphical desktop-sharing system) client that runs well in any modern browser.
How to connect
- Click on the link that you received by the school organizers or copy and paste it in the url bar of your favorite browser.
- Click on the connect button and insert the password.
Your browser will become a linux desktop
How to load the Yambo code and the tutorials
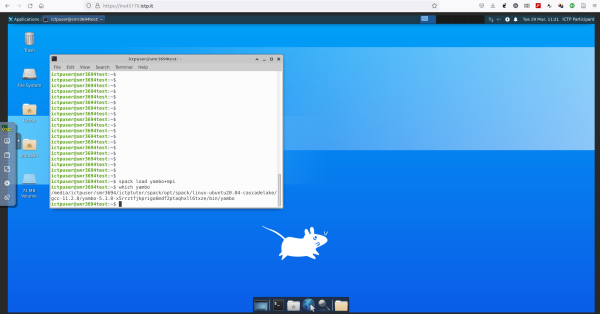
(i) Open a terminal (click on the black terminal icon, the second from the left in the lower part of the screen) and load the yambo code via spack:
spack load yambo
(ii) The tutorial material is available for the copy from this path:
cp -r /media/ictpuser/smr3694/ictptutor/YAMBO_TUTORIALS ~/
(iii) One of the tutorial shows the usage of Yambopy, it is installed via Anaconda. Yambopy is used both to manage workflows and to do postprocessing. So, in order to use it you have to load three spack pakages:
spack load quantum-espresso spack load yambo spack load anaconda3
Other useful spack commands
In the virtual machine Yambo was installed via the Spack tool. Spack is a package manager for supercomputers, Linux, and macOS. It makes installing scientific software easy.
spack find [options] [package]
List and search installed packages.
Useful options can be:
-p: show paths to package install directories -v: show variants in output (can be long)
An example:
ictpuser@smr3694test:~$ spack find -v yambo ==> 1 installed package -- linux-ubuntu20.04-cascadelake / gcc@11.2.0 ------------------- yambo@5.1.0~cuda~dp+mpi+openmp~parallel_io+ph+rt~yambopy cuda_arch=none linalg=slepc patches=b9362020b0a29abec535afd7d782b8bb643678fe9215815ca8dc9e4941cb169f,e3dcb3df39e2c70ebd57ded322d4ddbc1e23bf3b521541d29d4ea0377c475059 profile=memory,time
Variants are the way Spack calls the packages' installation options. The command used to have info about a package and its variants is:
spack info <package>
An example:
ictptutor@smr3694test:~/YAMBO_TUTORIALS$ spack info yambo AutotoolsPackage: yambo
Description: YAMBO is an open-source code released within the GPL licence. YAMBO implements Many-Body Perturbation Theory (MBPT) methods (such as GW and BSE) and Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory (TDDFT), which allows for accurate prediction of fundamental properties as band gaps of semiconductors, band alignments, defect quasi-particle energies, optics and out-of-equilibrium properties of materials. The code resorts to previously computed electronic structure, usually at the Density Functional Theory (DFT) level and for this reason it is interfaced with two of the most used planewave DFT codes used in scientific community, Quantum ESPRESSO and Abinit.
Homepage: http://www.yambo-code.org/index.php
Maintainers: @nicspalla
Externally Detectable: False
Tags: None
Preferred version: 5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master
Safe versions: 5.1.0 [git] https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo.git on branch master 5.0.4 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.4.tar.gz 5.0.3 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.3.tar.gz 5.0.2 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.2.tar.gz 5.0.1 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.1.tar.gz 5.0.0 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/5.0.0.tar.gz 4.5.3 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.5.3.tar.gz 4.5.2 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.5.2.tar.gz 4.5.1 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.5.1.tar.gz 4.5.0 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.5.0.tar.gz 4.4.1 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.4.1.tar.gz 4.3.3 https://github.com/yambo-code/yambo/archive/4.3.3.tar.gz
Deprecated versions: None
Variants: Name [Default] When Allowed values Description ================= ============= ==================== =========================================================================
cuda [off] -- on, off Build with CUDA
cuda_arch [none] -- none, 75, 70, 35, CUDA architecture
86, 72, 60, 21, 10,
80, 13, 53, 20, 62,
32, 30, 11, 61, 52,
37, 50, 12
dp [off] -- on, off Enable double precision
linalg [none] -- none, parallel, Activate additional support for linear algebra:
slepc "parallel" uses SCALAPACK and "slepc" is used for diagonalization of BSE
mpi [on] -- on, off Enable MPI support
openmp [off] -- on, off Enable OpenMP support
parallel_io [off] @4.4.0:+mpi on, off Activate the HDF5 parallel I/O
ph [off] -- on, off Compile PH executables
profile [none] -- none, time, memory Activate profiling of specific sections
rt [off] -- on, off Compile RT executables
yambopy [off] -- on, off Install Yambopy package
Installation Phases: autoreconf configure build install
Build Dependencies: blas cuda fftw-api gnuconfig hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc
Link Dependencies: blas cuda fftw-api hdf5 lapack libxc mpi netcdf-c netcdf-fortran netlib-lapack openmpi petsc py-yambopy scalapack slepc
Run Dependencies: None
Virtual Packages: None