First steps: walk through from DFT(standalone)
In this tutorial you will learn how to calculate optical spectra using Yambo, starting from a DFT calculation and ending with a look at local field effects in the optical response.
System characteristics
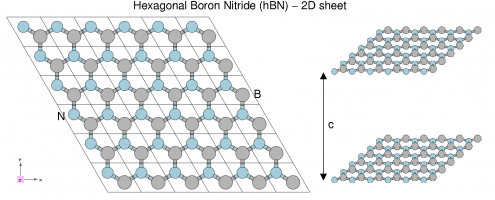
We will use a 3D system (bulk hBN) and a 2D system (hBN sheet).
Hexagonal boron nitride - hBN:
- HCP lattice, ABAB stacking
- Four atoms per cell, B and N (16 electrons)
- Lattice constants: a = 4.716 [a.u.], c/a = 2.582
- Plane wave cutoff 40 Ry (~1500 RL vectors in wavefunctions)
- SCF run: shifted 6x6x2 grid (12 k-points) with 8 bands
- Non-SCF run: gamma-centred 6x6x2 (14 k-points) grid with 100 bands
Prerequisites
You will need:
- PWSCF input files and pseudopotentials for hBN bulk
pw.xexecutable, version 5.0 or laterp2yandyamboexecutablesgnuplotfor plotting spectra
Download the Files
Download and unpack the followint files: hBN.tar.gz [15 MB], hBN-2D.tar.gz [8,6 MB]
In the next days you will also use this file which you may like to download now hBN-convergence-kpoints.tar.gz [254 MB]
After downloading the tar.gz files just unpack them in the YAMBO_TUTORIALS folder. For example
$ mkdir YAMBO_TUTORIALS $ mv hBN.tar.gz YAMBO_TUTORIALS $ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS $ tar -xvfz hBN.tar.gz $ ls YAMBO_TUTORIALS hBN
(Advanced users can download and install all tutorial files using git. See the main Tutorial Files page.)
DFT calculation of bulk hBN and conversion to Yambo
In this module you will learn how to generate the Yambo SAVE folder for bulk hBN starting from a PWscf calculation.
Conversion to Yambo format
The PWscf bBN.save output is converted to the Yambo format using the p2y executable (pwscf to yambo), found in the yambo bin directory.
Enter hBN.save and launch p2y:
$ cd hBN.save $ p2y ... <---> DBs path set to . <---> Index file set to data-file.xml <---> Header/K-points/Energies... done ... <---> == DB1 (Gvecs and more) ... <---> ... Database done <---> == DB2 (wavefunctions) ... done == <---> == DB3 (PseudoPotential) ... done == <---> == P2Y completed ==
This output repeats some information about the system and generates a SAVE directory:
$ ls SAVE ns.db1 ns.wf ns.kb_pp_pwscf ns.wf_fragments_1_1 ... ns.kb_pp_pwscf_fragment_1 ...
These files, with an n prefix, indicate that they are in netCDF format, and thus not human readable. However, they are perfectly transferable across different architectures. You can check that the databases contain the information you expect by launching Yambo using the -D option:
$ yambo -D [RD./SAVE//ns.db1]------------------------------------------ Bands : 100 K-points : 14 G-vectors [RL space]: 8029 Components [wavefunctions]: 1016 ... [RD./SAVE//ns.wf]------------------------------------------- Fragmentation :yes ... [RD./SAVE//ns.kb_pp_pwscf]---------------------------------- Fragmentation :yes - S/N 006626 -------------------------- v.04.01.02 r.00000 -
In practice we suggest to move the SAVE folder into a new clean folder.
In this tutorial however, we ask instead that you continue using a SAVE folder that we prepared previously:
$ cd ../../YAMBO $ ls SAVE
Initialization of Yambo databases
Use the SAVE folders that are already provided, rather than any ones you may have generated previously.
Every Yambo run must start with this step. Go to the folder containing the hBN-bulk SAVE directory:
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/YAMBO $ ls SAVE
TIP: do not run yambo from inside the SAVE folder!
This is the wrong way ..
$ cd SAVE $ yambo yambo: cannot access CORE database (SAVE/*db1 and/or SAVE/*wf)
In fact, if you ever see such message: it usually means you are trying to launch Yambo from the wrong place.
$ cd ..
Now you are in the proper place and
$ ls SAVE
you can simply launch the code
$ yambo
This will run the initialization (setup) runlevel.
Run-time output
This is typically written to standard output (on screen) and tracks the progress of the run in real time:
<---> [01] MPI/OPENMP structure, Files & I/O Directories <---> [02] CORE Variables Setup <---> [02.01] Unit cells <---> [02.02] Symmetries <---> [02.03] Reciprocal space <---> Shells finder |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> [02.04] K-grid lattice <---> Grid dimensions : 6 6 2 <---> [02.05] Energies & Occupations <---> [03] Transferred momenta grid and indexing <---> BZ -> IBZ reduction |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> [03.01] X indexes <---> X [eval] |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> X[REDUX] |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> [03.01.01] Sigma indexes <---> Sigma [eval] |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> Sigma[REDUX] |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> [04] Timing Overview <---> [05] Memory Overview <---> [06] Game Over & Game summary
Specific runlevels are indicated with numeric labels like [02.02].
The hashes (#) indicate progress of the run in Wall Clock time, indicating the elapsed (E) and expected (X) time to complete a runlevel, and the percentage of the task complete.
New core databases
New databases appear in the SAVE folder:
$ ls SAVE ns.db1 ns.wf ns.kb_pp_pwscf ndb.gops ndb.kindx ns.wf_fragments_1_1 ... ns.kb_pp_pwscf_fragment_1 ...
These contain information about the G-vector shells and k/q-point meshes as defined by the DFT calculation.
In general: a database called ns.xxx is a static database, generated once by p2y, while databases called ndb.xxx are dynamically generated while you use yambo.
TIP: if you launch yambo, but it does not seem to do anything, check that these files are present.
Report file
A report file r_setup is generated in the run directory. This mostly reports information about the ground state system as defined by the DFT run, but also adds information about the band gaps, occupations, shells of G-vectors, IBZ/BZ grids, the CPU structure (for parallel runs), and so on. Some points of note:
[02.03] RL shells ================= Shells, format: [S#] G_RL(mHa) [S453]:8029(0.7982E+5) [S452]:8005(0.7982E+5) [S451]:7981(0.7982E+5) [S450]:7957(0.7942E+5) ... [S4]:11( 1183.) [S3]:5( 532.5123) [S2]:3( 133.1281) [S1]:1( 0.000000)
This reports the set of closed reciprocal lattice (RL) shells defined internally that contain G-vectors with the same modulus. The highest number of RL vectors we can use is 8029. Yambo will always redefine any input variable in RL units to the nearest closed shell.
[02.05] Energies [ev] & Occupations
===================================
Fermi Level [ev]: 5.112805
VBM / CBm [ev]: 0.000000 3.876293
Electronic Temp. [ev K]: 0.00 0.00
Bosonic Temp. [ev K]: 0.00 0.00
El. density [cm-3]: 0.460E+24
States summary : Full Metallic Empty
0001-0008 0009-0100
Indirect Gaps [ev]: 3.876293 7.278081
Direct Gaps [ev]: 4.28829 11.35409
X BZ K-points : 72
Yambo recalculates again the Fermi level (close to the value of 5.06 noted in the PWscf SCF calculation). From here on, however, the Fermi level is set to zero, and other eigenvalues are shifted accordingly. The system is insulating (8 filled, 92 empty) with an indirect band gap of 3.87 eV. The minimum and maximum direct and indirect gaps are indicated. There are 72 k-points in the full BZ, generated using symmetry from the 14 k-points in our user-defined grid.
TIP: You should inspect the report file after every run for errors and warnings.
Different ways of running yambo
We just run Yambo interactively.
Let's try to re-run the setup with the command
$ nohup yambo & $ ls l_setup nohup.out r_setup r_setup_01 SAVE
If Yambo is launched using a script, or as a background process, or in parallel, this output will appear in a log file prefixed by the letter l, in this case as l_setup. If this log file already exists from a previous run, it will not be overwritten. Instead, a new file will be created with an incrementing numerical label, e.g. l_setup_01, l_setup_02, etc. This applies to all files created by Yambo. Here we see that l_setup was created for the first time, but r_setup already existed from the previous run, so now we have r_setup_01 If you check the differences between the two you will notice that in the second run yambo is reading the previously created ndb.kindx in place of re-computing the indexes. Indeed the output inside l_setup does not show the timing for X and Sigma
As a last step we run the setup in parallel, but first we delete the ndb.kindx file
$ rm SAVE/ndb.kindx $ mpirun -np 4 yambo $ ls LOG l_setup nohup.out r_setup r_setup_01 r_setup_02 SAVE
There is now r_setup_02 In the case of parallel runs, CPU-dependent log files will appear inside a LOG folder, e.g.
$ ls LOG l_setup_CPU_1 l_setup_CPU_2 l_setup_CPU_3 l_setup_CPU_4
This behaviour can be controlled at runtime - see the Parallel tutorial for details.
2D hBN
Simply repeat the steps above. Go to the folder containing the hBN-sheet SAVE directory and launch yambo:
$ cd TUTORIALS/hBN-2D/YAMBO $ ls SAVE $ yambo
Again, inspect the r_setup file, output logs, and verify that ndb.gops and ndb.kpts have been created inside the SAVE folder.
You are now ready to use Yambo!
Yambo's command line interface
Yambo uses a command line interface to select tasks, generate input files, and control the runtime behaviour.
In this module you will learn how to select tasks, generate and modify input files, and control the runtime behaviour by using Yambo's command line interface.
Command line options are divided into uppercase and lowercase options:
- Lowercase: select tasks, generate input files, and (by default) launch a file editor
- Uppercase: modify Yambo's default settings, at run time and when generating input files
Lowercase and uppercase options can be used together.
Input file generator
First, move to the appropriate folder and initialize the Yambo databases if you haven't already done so.
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/YAMBO $ yambo (initialize)
Yambo generates its own input files: you just tell the code what you want to calculate by launching Yambo along with one or more lowercase options.
Allowed options
To see the list of runlevels and options, run yambo -h or better,
$ yambo -H This is yambo 4.4.0 rev.148 A shiny pot of fun and happiness [C.D.Hogan] -h :Short Help -H :Long Help -J <opt> :Job string identifier -V <opt> :Input file verbosity[opt=RL,kpt,sc,qp,io,gen,resp,all,par] -F <opt> :Input file -I <opt> :Core I/O directory -O <opt> :Additional I/O directory -C <opt> :Communications I/O directory -D :DataBases properties -W <opt> :Wall Time limitation (1d2h30m format) -Q :Don't launch the text editor -E <opt> :Environment Parallel Variables file -M :Switch-off MPI support (serial run) -N :Switch-off OpenMP support (single thread run) -i :Initialization -o <opt> :Optics [opt=(c)hi is (G)-space / (b)se is (eh)-space ] -k <opt> :Kernel [opt=hartree/alda/lrc/hf/sex](hf/sex only eh-space; lrc only G-space) -y <opt> :BSE solver [opt=h/d/s/(p/f)i](h)aydock/(d)iagonalization/(i)nversion -r :Coulomb potential -x :Hartree-Fock Self-energy and local XC -d :Dynamical Inverse Dielectric Matrix -b :Static Inverse Dielectric Matrix -p <opt> :GW approximations [opt=(p)PA/(c)HOSEX] -g <opt> :Dyson Equation solver[opt=(n)ewton/(s)ecant/(g)reen] -l :GoWo Quasiparticle lifetimes -a :ACFDT Total Energy -s :ScaLapacK test
Any time you launch Yambo with a lowercase option, Yambo will generate the appropriate input file (default name: yambo.in) and launch the vi editor.
Editor choice can be changed at configure; alternatively you can use the -Q run time option to skip the automatic editing (do this if you are not familiar with vi!):
$ yambo -x -Q yambo: input file yambo.in created $ emacs yambo.in or your favourite editing tool
Combining options
Multiple options can be used together to activate various tasks or runlevels (in some cases this is actually a necessity). For instance, to generate an input file for optical spectra including local field effects (Hartree approximation), do (and then exit)
$ yambo -o c -k hartree which switches on: optics # [R OPT] Optics chi # [R CHI] Dyson equation for Chi. Chimod= "Hartree" # [X] IP/Hartree/ALDA/LRC/BSfxc
To perform a Hartree-Fock and GW calculation using a plasmon-pole approximation, do (and then exit):
$ yambo -x -g n -p p which switches on: HF_and_locXC # [R XX] Hartree-Fock Self-energy and Vxc gw0 # [R GW] GoWo Quasiparticle energy levels ppa # [R Xp] Plasmon Pole Approximation em1d # [R Xd] Dynamical Inverse Dielectric Matrix
Each runlevel activates its own list of variables and flags.
Changing input parameters
Yambo reads various parameters from existing database files and/or input files and uses them to suggest values or ranges. Let's illustrate this by generating the input file for a Hartree-Fock calculation.
$ yambo -x
Inside the generated input file you should find:
EXXRLvcs = 3187 RL # [XX] Exchange RL components %QPkrange # [GW] QP generalized Kpoint/Band indices 1| 14| 1|100| %
The QPkrange variable (follow the link for a "detailed" explanation for any variable) suggests a range of k-points (1 to 14) and bands (1 to 100) based on what it finds in the core database SAVE/ns.db1, i.e. as defined by the DFT code.
Leave that variable alone, and instead modify the previous variable to EXXRLvcs= 1000 RL
Save the file, and now generate the input a second time with yambo -x. You will see:
EXXRLvcs= 1009 RL
This indicates that Yambo has read the new input value (1000 G-vectors), checked the database of G-vector shells (SAVE/ndb.gops), and changed the input value to one that fits a completely closed shell.
Last, note that Yambo variables can be expressed in different units. In this case, RL can be replaced by an energy unit like Ry, eV, Ha, etc. Energy units are generally better as they are independent of the cell size. Technical information is available on the Variables page.
The input file generator of Yambo is thus an intelligent parser, which interacts with the user and the existing databases. For this reason we recommend that you always use Yambo to generate the input files, rather than making them yourself.
Uppercase options
Uppercase options modify some of the code's default settings. They can be used when launching the code but also when generating input files.
Allowed options
To see the list of options, again do:
$ yambo -H
Tool: yambo 4.1.2 rev.14024
Description: A shiny pot of fun and happiness [C.D.Hogan]
-J <opt> :Job string identifier
-V <opt> :Input file verbosity
[opt=RL,kpt,sc,qp,io,gen,resp,all,par]
-F <opt> :Input file
-I <opt> :Core I/O directory
-O <opt> :Additional I/O directory
-C <opt> :Communications I/O directory
-D :DataBases properties
-W <opt> :Wall Time limitation (1d2h30m format)
-Q :Don't launch the text editor
-M :Switch-off MPI support (serial run)
-N :Switch-off OpenMP support (single thread run)
[Lower case options]
Command line options are extremely important to master if you want to use yambo productively. Often, the meaning is clear from the help menu:
$ yambo -F yambo.in_HF -x Make a Hartree -Fock input file called yambo.in_HF $ yambo -D Summarize the content of the databases in the SAVE folder $ yambo -I ../ Run the code, using a SAVE folder in a directory one level up $ yambo -C MyTest Run the code, putting all report, log, plot files inside a folder MyTest
Other options deserve a closer look.
Verbosity
Yambo uses many input variables, many of which can be left at their default values. To keep input files short and manageable, only a few variables appear by default in the inout file. More advanced variables can be switched on by using the -V verbosity option. These are grouped according to the type of variable. For instance, -V RL switches on variables related to G vector summations, and -V io switches on options related to I/O control. Try:
$ yambo -o c -V RL switches on: FFTGvecs= 3951 RL # [FFT] Plane-waves $ yambo -o c -V io switches on: StdoHash= 40 # [IO] Live-timing Hashes DBsIOoff= "none" # [IO] Space-separated list of DB with NO I/O. DB= ... DBsFRAGpm= "none" # [IO] Space-separated list of +DB to be FRAG and ... #WFbuffIO # [IO] Wave-functions buffered I/O
Unfortunately, -V options must be invoked and changed one at a time. When you are more expert, you may go straight to -V all, which turns on all possible variables. However note that yambo -o c -V all adds an extra 30 variables to the input file, which can be confusing: use it with care.
Job script label
The best way to keep track of different runs using different parameters is through the -J flag. This inserts a label in all output and report files, and creates a new folder containing any new databases (i.e. they are not written in the core SAVE folder). Try:
$ yambo -J 1Ry -V RL -x and modify to FFTGvecs = 1 Ry EXXGvecs = 1 Ry $ yambo -J 1Ry Run the code $ ls yambo.in SAVE o-1Ry.hf r-1Ry_HF_and_locXC 1Ry 1Ry/ndb.HF_and_locXC
This is extremely useful when running convergence tests, trying out different parameters, etc.
Exercise: use yambo to report the properties of all database files (including ndb.HF_and_locXC)