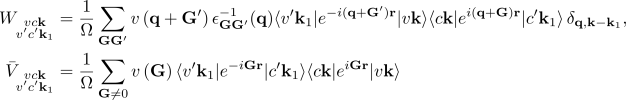Difference between revisions of "Bethe-Salpeter kernel"
| (19 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
To solve the Bethe-Salpeter equation the latter is usually rewritten in the space of transitions between valence and conduction states as the (pseudo)eigenvalue problem for a two-particle Hamiltonian. | To solve the Bethe-Salpeter equation, the latter is usually rewritten in the space of transitions between valence and conduction states as the (pseudo)eigenvalue problem for a two-particle Hamiltonian. | ||
For a non spin-polarized system and in the q=0 limit, the two-particle Hamiltonian matrix elements are given by | |||
[[File:BSE1-Eq1.png|none|x50px]] | [[File:BSE1-Eq1.png|none|x50px]] | ||
where ''vc'''''k''' indicates the pair of quasiparticle states ''v'''''k''' and ''c'''''k'''. | where ''vc'''''k''' indicates the pair of quasiparticle states ''v'''''k''' and ''c'''''k'''. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
[[File:BSE1_Eq3.png|none|x100px]] | [[File:BSE1_Eq3.png|none|x100px]] | ||
Here ε<sub>GG'</sub><sup>-1</sup> is the inverse of the dielectric screening matrix which was evaluated in the [[Static screening]] module | Here ε<sub>GG'</sub><sup>-1</sup> is the inverse of the dielectric screening matrix which was evaluated in the [[Static screening]] module. | ||
==Prerequisites== | ==Prerequisites== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
==Choosing input parameters== | ==Choosing input parameters== | ||
Generate the input file by invoking yambo with the option <code>-o b -k sex | Generate the input file by invoking yambo with the option <code>-o b -k sex</code> from the command line: | ||
$ yambo -o b -k sex | $ yambo -o b -k sex -F 02_3D_BSE_kernel.in -J 3D_BSE | ||
The input opens in the standard editor. The relevant input parameters to be changed are | The input opens in the standard editor. The relevant input parameters to be changed are | ||
[[Variables#BSENGexx|BSENGexx]] = | [[Variables#BSENGexx|BSENGexx]] = 30000 mRy | ||
[[Variables#BSENGBlk|BSENGBlk]] = | [[Variables#BSENGBlk|BSENGBlk]] = 4000 mRy | ||
% [[Variables#BSEBands|BSEBands]] | % [[Variables#BSEBands|BSEBands]] | ||
6 | 10 | | 6 | 10 | | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
The third parameter gives the range of quasiparticle states (their band index) that define the basis of quasiparticle pairs that we need to describe the excitons (in the energy range of interest). | The third parameter gives the range of quasiparticle states (their band index) that define the basis of quasiparticle pairs that we need to describe the excitons (in the energy range of interest). | ||
For example since we have 8 occupied bands, here we consider the pairs of bands: ''6-9'', ''6-10'', ''7-9'', ''7-10'', ''8-9'', ''8-10'' (those are 6 pairs of bands = | For example since we have 8 occupied bands, here we consider the pairs of bands: ''6-9'', ''6-10'', ''7-9'', ''7-10'', ''8-9'', ''8-10'' (those are 6 pairs of bands = 3 valence times 2 conduction bands). | ||
For each of those pairs we then consider all '''k''' points in the Brillouin zone available from the DFT calculations. Since we have a ''6 x 6 x 2'' grid, this amounts to 72 '''k''' points in the Brillouin zone. | For each of those pairs we then consider all '''k''' points in the Brillouin zone available from the DFT calculations. Since we have a ''6 x 6 x 2'' grid, this amounts to 72 '''k''' points in the Brillouin zone. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
Run the calculation by invoking yambo in the command line: | Run the calculation by invoking yambo in the command line: | ||
$ yambo -F 02_3D_BSE_kernel.in -J 3D_BSE | $ yambo -F 02_3D_BSE_kernel.in -J 3D_BSE | ||
In the log (either in standard output or in | In the log (either in standard output or in <code>l-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bse</code>), after various setup/loading, the kernel is calculated: | ||
<01s> [05. | <01s> [05.03.03] Main kernel loop | ||
<02s> Kernel |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) | <02s> Kernel |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) | ||
In the report | In the report <code>r-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bse</code> the information relative to this runlevel are reported under the section: | ||
[05] Bethe Salpeter Equation @q1 | |||
================================ | |||
<!-- | |||
[05] Response Functions in Transition space | [05] Response Functions in Transition space | ||
=========================================== | =========================================== | ||
(yambo 4.3) | |||
[05] BSE solver(s) @q1 | |||
========================= | |||
(yambo 4.5) | |||
--> | |||
Take some time to inspect the log and the report. For example try to find where the input parameters are reported, the dimension of the 2-particle Hamiltonian and if these match your expectations. | Take some time to inspect the log and the report. For example try to find where the input parameters are reported, the dimension of the 2-particle Hamiltonian and if these match your expectations. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 80: | ||
* How to compute the Bethe-Salpeter kernel | * How to compute the Bethe-Salpeter kernel | ||
== | ==Navigate== | ||
* Previous module: [[Static screening]] | * Previous module: [[Static screening]] | ||
* | * Next module: [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization | Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization]] | ||
* Back to [[Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide]] tutorial | * Back to [[Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide]] tutorial | ||
* [[Tutorials|Back to tutorials menu]] | * [[Tutorials|Back to tutorials menu]] | ||
| Line 136: | Line 147: | ||
value | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | # [EXTQP BSK BSS] E parameters (c/v) eV|adim|adim | value | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | # [EXTQP BSK BSS] E parameters (c/v) eV|adim|adim | ||
Note that if you know also the values of the conduction and valence | Note that if you know also the values of the conduction and valence stretching you can insert them instead of using the default values of 1. | ||
Instead if you have already generated a ndb.QP database for the full set of k-points and energies of the excitonic | Instead, if you have already generated a ndb.QP database for the full set of k-points and energies of the excitonic Hamiltonian, | ||
you can read it in this way | you can read it in this way | ||
Latest revision as of 12:56, 24 May 2023
In this module you will learn how to calculate the matrix elements of the Bethe-Salpeter kernels. This is a fundamental step in the calculation of optical spectra within the Bethe-Salpeter equation framework.
Background
To solve the Bethe-Salpeter equation, the latter is usually rewritten in the space of transitions between valence and conduction states as the (pseudo)eigenvalue problem for a two-particle Hamiltonian. For a non spin-polarized system and in the q=0 limit, the two-particle Hamiltonian matrix elements are given by
where vck indicates the pair of quasiparticle states vk and ck. The first term on the RHS is the quasiparticle energy differences (diagonal only). The second term is the kernel which is the sum of the electron-hole exchange part V (which stems from the Hartree potential) and the electron-hole attraction part W (which stems from the screened exchange potential). The kernel both shifts (diagonal contributions) and couples (off-diagonal contributions) the quasiparticle energy differences:
Here εGG'-1 is the inverse of the dielectric screening matrix which was evaluated in the Static screening module.
Prerequisites
- You must first complete the static screening module
You will need:
- The
SAVEdatabases for 3D hBN - The
3D_BSEdirectory with the databases generated in the static screening module - The
yamboexecutable
Choosing input parameters
Generate the input file by invoking yambo with the option -o b -k sex from the command line:
$ yambo -o b -k sex -F 02_3D_BSE_kernel.in -J 3D_BSE
The input opens in the standard editor. The relevant input parameters to be changed are
BSENGexx = 30000 mRy BSENGBlk = 4000 mRy % BSEBands 6 | 10 | %
The first two are the cutoff for the summations on the reciprocal lattice vectors which appear in the expressions for V (BSENGexx) and W (BSENGBlk) here above.
The third parameter gives the range of quasiparticle states (their band index) that define the basis of quasiparticle pairs that we need to describe the excitons (in the energy range of interest). For example since we have 8 occupied bands, here we consider the pairs of bands: 6-9, 6-10, 7-9, 7-10, 8-9, 8-10 (those are 6 pairs of bands = 3 valence times 2 conduction bands).
For each of those pairs we then consider all k points in the Brillouin zone available from the DFT calculations. Since we have a 6 x 6 x 2 grid, this amounts to 72 k points in the Brillouin zone.
Then finally we are using a basis of 6 x 72 = 432 vck pairs to represent the excitons of the system.
The values for these 3 parameters are chosen from convergence studies, as discussed in the next tutorial.
Bethe-Salpeter kernel runlevel
Run the calculation by invoking yambo in the command line:
$ yambo -F 02_3D_BSE_kernel.in -J 3D_BSE
In the log (either in standard output or in l-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bse), after various setup/loading, the kernel is calculated:
<01s> [05.03.03] Main kernel loop <02s> Kernel |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X)
In the report r-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bse the information relative to this runlevel are reported under the section:
[05] Bethe Salpeter Equation @q1 ================================
Take some time to inspect the log and the report. For example try to find where the input parameters are reported, the dimension of the 2-particle Hamiltonian and if these match your expectations.
This run does not produce any human readable output. The kernel is stored in a database in the 3D_BSE directory
3D_BSE/ndb.BS_Q1
Summary
From this tutorial you've learned:
- How to compute the Bethe-Salpeter kernel
- Previous module: Static screening
- Next module: Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization
- Back to Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide tutorial
- Back to tutorials menu
- Back to technical modules menu